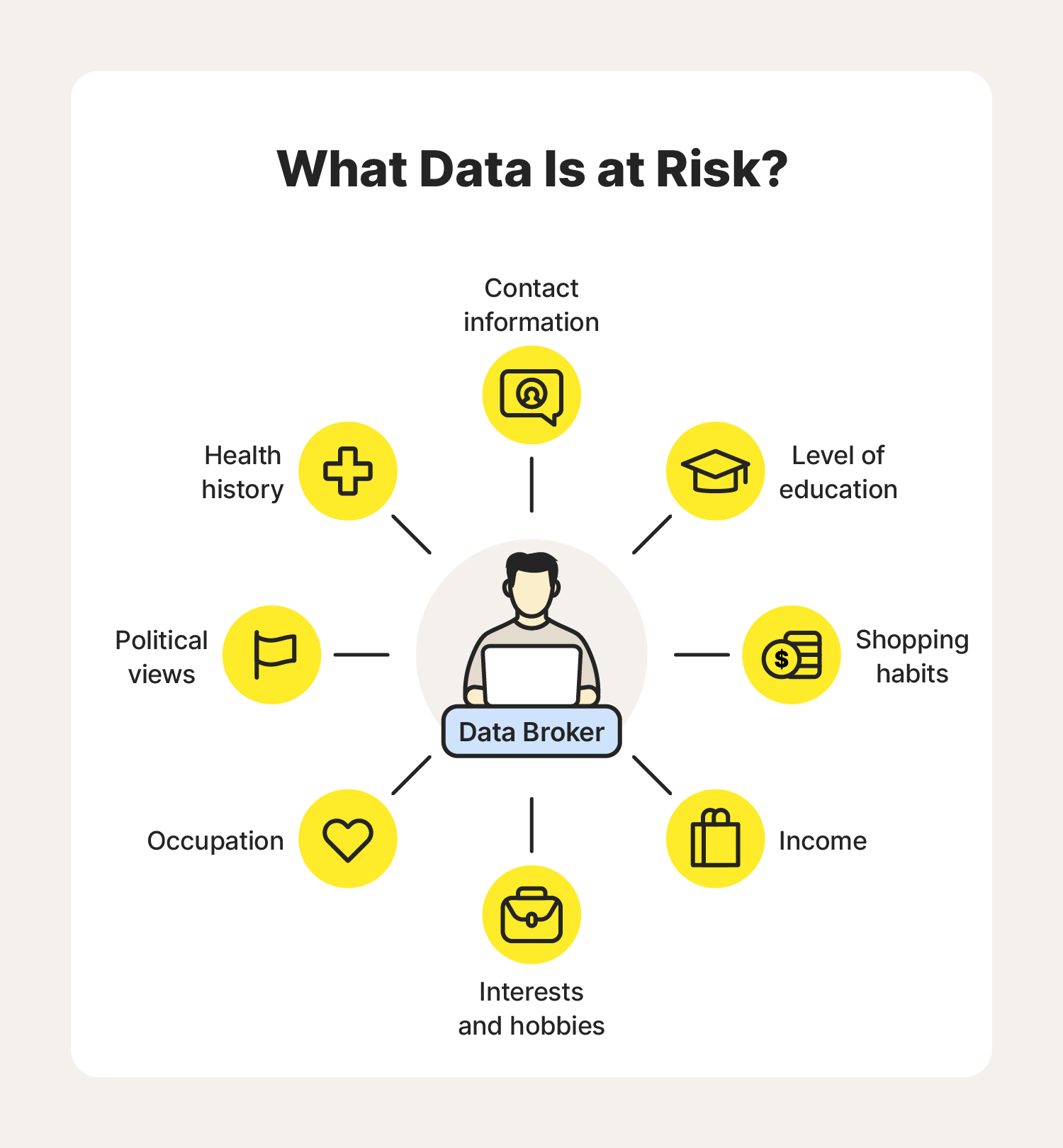
Data Brokers Who Are They And What Do They Do
In the digital age, the exchange of sensitive details has become a pivotal aspect of modern commerce and communication. This section delves into the activities of those entities often referred to as information intermediaries, exploring their functions and the implications for individual privacy and security.
These entities operate within a complex web of data transactions, facilitating the transfer of detailed records about individuals. Their activities are crucial to various sectors, including marketing, finance, and law enforcement, yet they also raise significant concerns regarding the safeguarding of personal details and the integrity of digital security measures.
As we navigate through this exploration, it becomes essential to understand not just the mechanics of how these intermediaries operate, but also the broader ethical and legal frameworks that govern their actions. This understanding is vital for anyone concerned about the protection of their own sensitive records and the broader implications for societal trust in digital platforms.
Defining the Role of Data Brokers
This section delves into the specific functions and responsibilities of entities that specialize in the collection and distribution of user details. It aims to clarify how these organizations operate within the broader context of digital commerce and user privacy management.
Key Functions of Information Aggregators
Information aggregators play a pivotal role in modern digital economies. Primarily, they gather extensive sets of user data, which can include anything from shopping habits to online browsing patterns. This data is then processed and often sold to various businesses, marketers, and researchers, who utilize it to tailor their services or products more effectively to consumer needs.
Data Collection and Its Implications
The methods employed by these aggregators range from purchasing data from other entities to scraping public records and even tracking online activities. This extensive collection has significant implications for individual privacy and the ethical use of personal data. Understanding these practices is crucial for consumers and policymakers alike in crafting effective strategies to protect personal privacy.
Regulatory Compliance and Ethical Considerations
As the role of information aggregators continues to evolve, so too does the regulatory landscape governing their activities. Compliance with data protection laws and ethical guidelines is essential not only for the legal operation of these businesses but also for maintaining public trust. This section will explore how current regulations impact the operations of these entities and what changes might be necessary to better safeguard user privacy.
In conclusion, the role of information aggregators is multifaceted, encompassing data collection, processing, and distribution. Their activities have profound effects on both the commercial landscape and individual privacy rights. As such, a thorough understanding of their operations is vital for anyone concerned with the future of digital privacy and ethical data use.
Defining the Role of Data Brokers
This section delves into the pivotal role that information intermediaries play in the modern digital ecosystem. By examining their functions and the scope of their operations, we gain a deeper understanding of how these entities influence the flow of data and its implications for user confidentiality.
Information intermediaries, often referred to as data brokers, operate at the intersection of data collection and distribution. Their primary function is to gather, analyze, and sell data, which is then used by various businesses and organizations for targeted marketing, risk assessment, and other strategic purposes. The evolution of these entities has been shaped by technological advancements and the increasing demand for data-driven insights.
| Time Period | Key Developments |
|---|---|
| Early 2000s | Emergence of online data aggregation services focusing on consumer behavior. |
| Mid 2000s | Expansion into more sophisticated data analytics and integration of offline data sources. |
| Late 2000s to 2010s | Growth in data privacy concerns leading to regulatory scrutiny and industry self-regulation. |
| 2020s | Advancements in AI and machine learning reshaping data collection and analysis methods. |
The origins of data brokerage can be traced back to the early days of direct marketing, where companies collected and utilized mailing lists. Over time, this practice evolved into a more complex industry involving vast amounts of data and sophisticated analytical tools. The transformation of data brokerage into a significant sector within the digital economy reflects the growing importance of data in contemporary business practices.
Understanding the historical trajectory of data brokerage helps in contextualizing its current practices and anticipating future developments. As technology continues to advance, the role of these intermediaries is likely to become even more integral to the functioning of the global digital marketplace.
Origins and Evolution of Data Brokerage
This section delves into the historical development and transformation of the industry that specializes in the collection and distribution of user details. Understanding the roots and progression of this sector is crucial for grasping its current dynamics and implications.
- Early Beginnings: Initially, the gathering of user details was a fragmented activity, often conducted by various local entities for specific purposes such as marketing or demographic analysis.
- Technological Advancements: The advent of computers and later the internet significantly transformed the scale and efficiency of data collection. This era marked the shift from manual to automated data processing, enabling larger volumes of information to be handled and analyzed.
- Expansion of Scope: Over time, the focus expanded from basic demographic data to include more detailed behavioral and transactional information. This broadening scope was driven by the increasing demand for personalized marketing and targeted advertising.
- Emergence of Specialized Firms: As the industry matured, specialized firms emerged that focused solely on the acquisition, aggregation, and sale of user details. These entities became pivotal in the data ecosystem, facilitating the exchange of information between various stakeholders.
- Regulatory Challenges: The growth of this sector also brought about significant regulatory challenges, as concerns over user privacy and data security became more pronounced. This led to the development of various legal frameworks aimed at regulating the activities of these firms.
- Current Landscape: Today, the industry is characterized by sophisticated data management techniques and a complex web of data sharing agreements. The ongoing evolution is marked by continuous adaptation to technological advancements and regulatory changes.
Understanding the historical trajectory of this industry provides a foundation for assessing its current practices and future directions. It highlights the interplay between technological innovation, market demands, and regulatory oversight, shaping the landscape of data management and user privacy.
Methods of Data Acquisition and Aggregation
This section delves into the various strategies employed by entities to gather and compile data. It explores the mechanisms through which these organizations collect vast amounts of user details, often without direct interaction with the individuals involved. Understanding these methods is crucial for comprehending the scale and scope of data collection practices prevalent today.
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Public Records | Data is sourced from government records that are publicly available. | Property records, court documents, and voter registration lists. |
| Web Scraping | Automated tools are used to extract information from websites. | Extracting user reviews or profiles from social media platforms. |
| Data Sharing Agreements | Entities exchange data with each other under mutual agreements. | Credit card companies sharing transaction data with marketing firms. |
| Surveys and Forms | Data is collected through voluntary submissions by individuals. | Online surveys or registration forms on websites. |
| Purchase from Third Parties | Data is bought from other companies that specialize in data collection. | Buying email lists from companies that gather email addresses. |
Each of these methods has its own implications for the privacy and security of the individuals whose data is being collected. It is essential for consumers and regulatory bodies to understand these practices to ensure appropriate safeguards are in place to protect personal data.
In conclusion, the methods of data acquisition and aggregation are diverse and pervasive, highlighting the need for robust frameworks to regulate and monitor these activities. As technology evolves, so too must the strategies to protect individual privacy and data integrity.
Methods of Data Acquisition and Aggregation
This section delves into the intricate processes employed by entities in the information trade to gather and compile vast amounts of details. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for grasping the scale and impact of the operations involved in the collection of user data.
Data Collection Techniques
Entities in the information trade utilize a variety of methods to amass data. These include but are not limited to, web scraping, which involves automated software that extracts information from websites. Additionally, these entities often purchase data from other businesses or obtain it through partnerships, where they exchange resources or services for access to databases.
Data Aggregation Strategies
Once the data is collected, the next step involves aggregation. This process entails combining data from various sources to create a comprehensive profile. Techniques such as data fusion and integration are commonly used to enhance the accuracy and utility of the information. The aggregated data is then typically stored in centralized databases, which are meticulously organized to facilitate easy access and analysis.
Impact on Data Integrity and Privacy
The methods of acquisition and aggregation can significantly impact the integrity of the data and the privacy of individuals. It is essential to consider the ethical implications and the potential for misuse of such comprehensive data sets. Regulatory frameworks and consumer protection measures are continually evolving to address these concerns, ensuring that the practices of information trade entities align with legal and ethical standards.
The Business Model of Data Brokers
This section delves into the economic strategies employed by entities that specialize in the collection and distribution of user details. It explores how these organizations generate revenue and maintain their operations in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
At the core of these entities' operations is the acquisition of vast arrays of user data. This data is then meticulously sorted and categorized, often without the direct knowledge or consent of the individuals involved. The primary sources of income for these firms include the sale of this aggregated data to third parties, who use it for various purposes such as targeted advertising, risk assessment, and market analysis.
Additionally, these entities may offer premium services that provide more detailed or specific user information. This can include enhanced analytics tools or customized data sets tailored to the needs of particular clients. The business model is thus built on a dual-pronged approach: the bulk sale of general data and the provision of specialized services for more discerning customers.
The sustainability of this model relies heavily on the continuous flow of data. To ensure this, these entities employ sophisticated techniques for data harvesting, including the use of cookies, tracking pixels, and other digital surveillance methods. They also engage in partnerships with various online platforms and service providers to access user data directly.
Regulatory compliance plays a crucial role in shaping the business model of these entities. As laws and regulations evolve to protect user privacy, these firms must adapt their practices to avoid legal repercussions. This includes implementing measures to anonymize data and ensuring transparency in their data collection and usage practices.>
In conclusion, the business model of these data-centric entities is multifaceted, involving complex data management strategies, regulatory adherence, and innovative approaches to data monetization. Understanding this model is essential for comprehending the broader implications of data collection and its impact on digital privacy.
Impact on Individual Privacy
This section delves into the profound effects that the activities of information intermediaries have on the confidentiality of individuals' details. It explores how these entities, through their collection and distribution practices, influence the safeguarding of sensitive data.
The operations of these intermediaries are multifaceted, often involving the gathering of vast amounts of user data from various sources. This data is then processed and sold to third parties, which can include marketers, financial institutions, and even governmental bodies. The implications of such practices are far-reaching and can significantly impact the privacy of individuals.
- **Unauthorized Access**: One major concern is the potential for unauthorized access to personal details. This can occur when data is not adequately protected or when it is shared without proper consent.
- **Data Misuse**: There is also the risk of data misuse, where collected information is used in ways that were not intended by the individuals it pertains to.
- **Surveillance and Tracking**: These practices can lead to increased surveillance and tracking, affecting personal freedoms and the right to anonymity.
Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in mitigating these risks. They establish guidelines and standards that these intermediaries must adhere to in order to protect individual privacy. These frameworks vary by region and can include laws that mandate transparency in data handling, require explicit consent for data collection, and impose penalties for non-compliance.
- **Transparency Requirements**: Regulations often require these entities to clearly disclose their data collection practices.
- **Consent Provisions**: Laws may stipulate that individuals must give explicit consent before their data can be collected or used.
- **Enforcement Mechanisms**: Robust enforcement mechanisms are necessary to ensure compliance with these regulations, including fines and other legal sanctions.
Understanding and implementing these regulatory measures is essential for protecting the privacy of individuals in the digital age. It is also important for consumers to be aware of these issues and to take proactive steps to safeguard their own data.
Regulatory Frameworks Governing Data Brokers
This section delves into the complex landscape of legal and regulatory measures that aim to oversee the activities of entities involved in the collection and distribution of user data. The focus is on understanding how these frameworks are designed to protect individual rights and ensure transparency in the operations of such entities.
Regulatory oversight in this domain is crucial as it directly impacts the safeguarding of personal details and the maintenance of ethical standards in data handling. Here, we explore various aspects of these regulations, including their scope, enforcement mechanisms, and effectiveness in curbing potential abuses.
- Legislative Basis: Many countries have enacted specific laws that govern the collection, storage, and dissemination of user data. These laws often outline clear guidelines and penalties for non-compliance.
- Enforcement Agencies: Various governmental bodies are tasked with the enforcement of these regulations. Their roles include monitoring compliance, investigating violations, and imposing sanctions when necessary.
- International Cooperation: Given the global nature of data flows, international cooperation is essential. This involves sharing information and coordinating enforcement actions across borders.
- Consumer Rights: Regulations also focus on empowering consumers by ensuring they are informed about how their data is used and granting them rights to control over their personal details.
- Technological Challenges: The rapid evolution of technology presents ongoing challenges. Regulations must continually adapt to new forms of data collection and distribution methods.
In conclusion, the regulatory frameworks governing these entities are a critical component in the fight to protect individual privacy and ensure ethical data practices. As technology continues to evolve, so too must these frameworks to remain effective and relevant.
Consumer Awareness and Protection Measures
This section delves into the strategies and initiatives aimed at enhancing public understanding and safeguarding against potential risks associated with the collection and use of consumer data. It explores various methods through which individuals can protect their digital footprints and advocates for increased transparency in the data industry.
- Education and Awareness Campaigns: Efforts to educate the public about the importance of data protection are crucial. These campaigns can range from simple tips on managing online privacy settings to more complex discussions about the implications of data sharing.
- Legislation and Regulation: Governments around the world are implementing stricter laws to regulate the data industry. These regulations aim to protect consumer rights and ensure that companies handle data responsibly.
- Technological Solutions: Innovations in technology offer new ways to protect personal data. Tools such as encryption and anonymization techniques can help safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Consumer Empowerment: Encouraging consumers to take an active role in managing their data is essential. This includes providing them with the tools and knowledge to make informed decisions about their data usage and sharing.
- Transparency in Data Practices: Companies are increasingly being held accountable for their data practices. This includes clear communication about what data is collected, how it is used, and who it is shared with.
As we look to the future, the focus on consumer protection will continue to evolve, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. It is imperative that these measures keep pace with the rapid developments in the data industry to ensure ongoing protection and awareness.
Future Trends in Data Brokerage and Privacy
In this section, we delve into the anticipated developments within the realm of information management and safeguarding individual rights. As technology continues to evolve, so too do the strategies and regulations surrounding the collection and use of sensitive data. This exploration aims to forecast how these changes might shape the landscape of data handling and privacy protection in the coming years.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are set to redefine the methods by which data is analyzed and utilized. These technologies promise more sophisticated data processing capabilities, which could lead to enhanced personalization of services but also raise concerns about the depth of intrusion into personal lives. The balance between utility and privacy will be a critical area of focus, with ongoing debates on the ethical use of AI in data analysis.
Regulatory Shifts
Expect to See this guide on Medium a tightening of regulations around data protection, mirroring the global trend towards stricter privacy laws. The implementation of comprehensive frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, signals a move towards more stringent controls on data handling. These regulations are likely to influence global standards, prompting companies worldwide to reassess their data collection and management practices.
Consumer Awareness and Activism
As awareness grows about the value and vulnerability of personal data, consumers are becoming more proactive in demanding transparency and control over their information. This shift in consumer behavior is driving businesses to adopt more ethical practices and to be more accountable. The future may see a rise in consumer-led initiatives and technologies that empower individuals to manage and protect their data more effectively.
Innovation in Data Security
The continuous evolution of cybersecurity threats necessitates ongoing innovation in data protection methods. From advanced encryption techniques to decentralized data storage solutions, the security landscape is rapidly evolving. These innovations aim to provide robust defenses against data breaches and unauthorized access, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure in an increasingly digital world.
In conclusion, the future of data management and privacy is poised for significant transformations, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and heightened consumer awareness. Balancing the benefits of data utilization with the imperative to protect individual rights will remain a central challenge and focus in the years to come.